Lab Setup / COE'S
ROBOTICS & AUTOMATION
Robotics and Automation is a multidisciplinary field that merges mechanical engineering, electrical systems, computer science, and artificial intelligence to develop systems capable of executing tasks with minimal or no human input. Robotics focuses on the design, construction, operation, and application of robots—machines that can carry out physical actions autonomously or with limited control. Automation, on the other hand, utilizes control systems, software, and advanced technologies to manage processes efficiently, ensuring improved speed, accuracy, and reliability across a wide range of industries. In healthcare, robotic systems support surgeons in performing complex operations with enhanced precision. As technology continues to advance, Robotics and Automation are expected to play an even greater role in shaping the future of work, productivity, and daily life.
INTERNET OF THINGS (IOT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the ever-growing network of physical objects or "things" that are embedded with sensors, software, and various other technologies. These components allow the devices to connect, communicate, and share data with other devices and systems over the internet without requiring human-to-human or human-to-computer interaction. These connected objects can include a wide range of items, such as household appliances, smart thermostats, wearable fitness devices, security systems, and even medical equipment. Beyond consumer applications, IoT also plays a vital role in industries like manufacturing, transportation, agriculture, and healthcare, where connected machines and sensors help monitor operations, improve efficiency, and enable real-time decision-making. As IoT technology continues to evolve, it is driving innovation, automation.
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI)
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, particularly computer systems. These processes include learning (the acquisition of information and rules for using it), reasoning (using rules to reach approximate or definite conclusions), and self-correction. AI encompasses a broad range of technologies and techniques, including machine learning, natural language processing, computer vision, robotics, and expert systems, among others. AI is increasingly being integrated into everyday applications such as virtual assistants, recommendation engines, autonomous vehicles, and fraud detection systems. In industries like healthcare, AI aids in diagnostics and personalized treatment, while in finance, it powers algorithmic trading and risk management. As AI continues to evolve, it promises to transform the way we work, interact, and make decisions—bringing smarter.
DRONE TECHNOLOGY
Drone technology refers to the design, development, operation, and application of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), commonly known as drones. Drones are aircraft that are operated without a human pilot onboard and can be remotely controlled or operate autonomously based on pre-programmed instructions or artificial intelligence algorithms. Drone technology encompasses a wide range of platforms, sizes, capabilities, and applications, from small consumer drones to large military-grade UAVs. Drones are increasingly used in fields such as agriculture for crop monitoring and spraying, logistics for aerial deliveries, filmmaking for capturing dynamic footage, and disaster management for search and rescue operations. . As technology continues to advance, drones are becoming smarter, more efficient, and more accessible, paving the way for innovative uses across both commercial and public sectors.
INDUSTRY 4.0
Industry 4.0, also known as the fourth industrial revolution, refers to the ongoing transformation of traditional manufacturing and industrial practices through the integration of digital technologies. This concept encompasses a range of technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), robotics, additive manufacturing (3D printing), big data analytics, cloud computing, augmented reality (AR), and cyber-physical systems. By connecting machines, systems, and humans, Industry 4.0 enables smarter factories with enhanced automation, real-time data exchange, and improved operational efficiency. This shift leads to greater flexibility in production, reduced costs, and faster time-to-market for new products. As businesses continue to adopt these advanced technologies, Industry 4.0 is reshaping the future of manufacturing, driving innovation and competitiveness on a global scale.
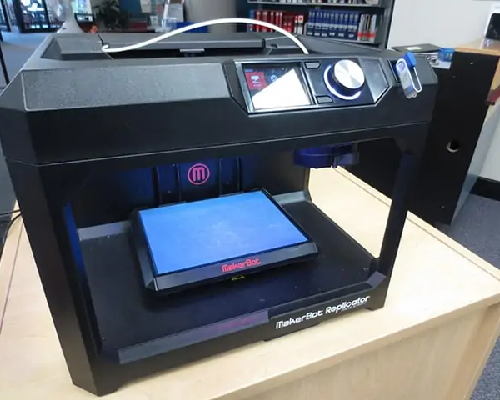
ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING
Additive manufacturing, often referred to as 3D printing, is a revolutionary manufacturing process that builds objects layer by layer from digital 3D models. Unlike traditional subtractive manufacturing methods, which involve cutting away material from a solid block, additive manufacturing adds material layer upon layer until the desired object is formed. This layer-by-layer approach offers numerous advantages, including the ability to create complex geometries, reduce material waste, and customize products on-demand. Additive manufacturing is used across various industries such as aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and consumer goods. It enables rapid prototyping, reduces production lead times, and allows for lightweight yet strong parts that are difficult to produce with conventional techniques. As the technology advances, 3D printing continues .
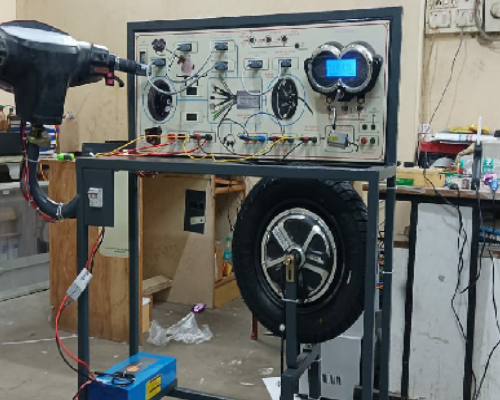
ELECTRIC VEHICLE (EV LAB)
Our EV Lab is a specialized hub driving innovation and development in electric mobility. It serves as a focal point for advancing electric vehicle technology, focusing on key areas such as battery efficiency, charging infrastructure, and vehicle design. By bringing together expertise from diverse disciplines, the lab leads the evolution of electric vehicles through groundbreaking research, collaboration with industry and academia, and advocacy for policies that promote widespread EV adoption. The lab also provides state-of-the-art testing facilities, educational programs, and policy guidance to accelerate the development and deployment of sustainable transportation solutions. By fostering innovation and empowering stakeholders, the EV Lab plays a crucial role in driving the global transition to cleaner, more efficient mobility, shaping a greener future for communities worldwide.
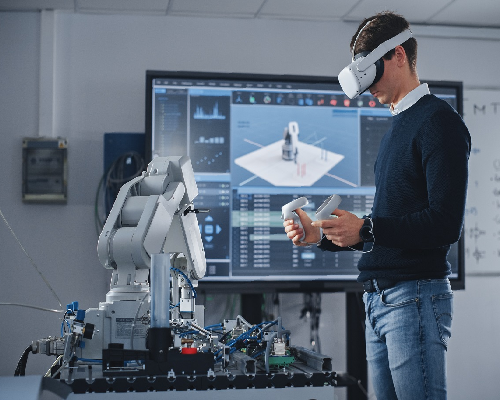
AR & VR BASED VIRTUAL LAB
This Scope of Work (SOW) outlines the objectives, deliverables, and responsibilities for setting up an Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) Lab, with an optional Mixed Reality (MR) component. The lab will be designed and equipped to support training, education, research, and development in AR, VR, and MR technologies. The lab aims to provide immersive learning experiences, facilitate innovation, and engineering, and entertainment. By integrating cutting-edge hardware and software, this facility will foster collaboration and skill-building, preparing users to leverage the full potential of extended reality technologies.
1. To establish a state-of-the-art AR/VR/MR Lab
2. To Provide hardware and software required for AR/VR/MR development.
3. To integrate Mixed Reality capabilities.
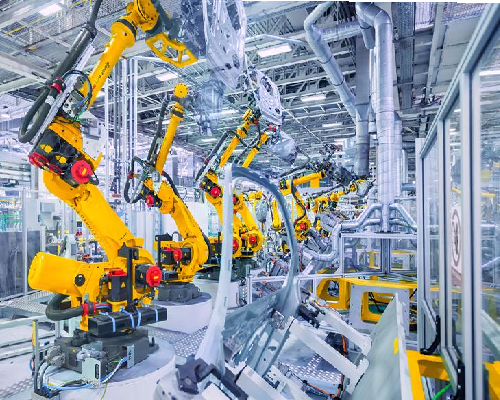
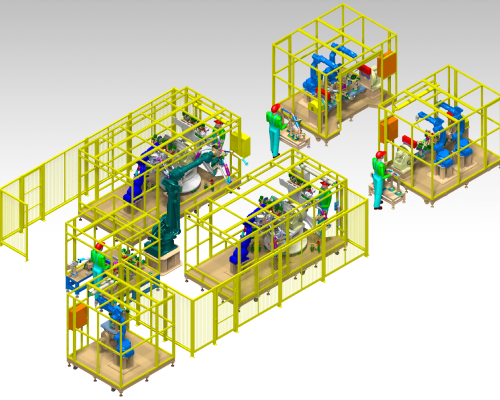
INDUSTRIAL ROBOTICS
Industrial robotics refers to the use of robotic systems in manufacturing and industrial settings to automate tasks traditionally performed by human workers. These robotic systems are designed to perform a variety of repetitive, dangerous, or precise tasks with high efficiency, accuracy, and reliability. Industrial robots are equipped with sensors, actuators, and programming capabilities that allow them to manipulate objects, move along predefined paths, and interact with their environment. They are widely employed in industries such as automotive manufacturing, electronics assembly, and packaging, where they help increase productivity, reduce labor costs, and improve workplace safety. With advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning, industrial robots are becoming more adaptable and capable of handling complex tasks, driving innovation and flexibility in modern manufacturing processes.
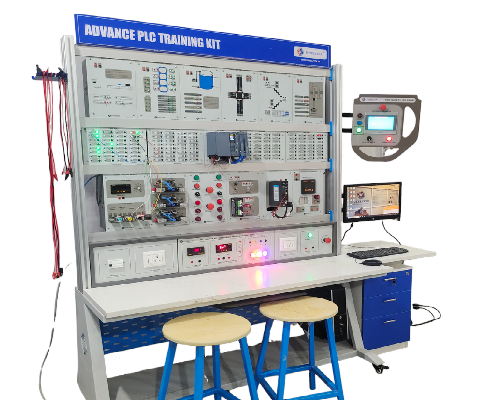
PLC TRAINER KIT
The customized PLC training kit enables students to gain hands-on experience with PLC programming languages and HMI programming. It provides practical exposure to communication protocols such as Modbus, Ethernet, and CANopen. The kit includes both digital and analogue I/O modules, allowing students to measure signals and create logical control conditions, thereby enhancing their understanding of industrial automation systems. This comprehensive training tool helps students develop critical skills needed in automation industries, including troubleshooting, system integration, and control logic design. By working with real-world components and protocols, learners can better prepare for careers in manufacturing, process control, robotics, and smart factories. The hands-on nature of the kit fosters problem-solving abilities and deepens technical knowledge.